Last week we reviewed what Illinois was like during the latter 1600s, when the French first encountered the Illiniwek Confederation and began to explore and settle the Illinois Country.
France had laid claim to a vast territory in North America, where France’s colonial rivals England, Holland, and Spain also were building empires. As these European powers strove with each other, the ways of life of the native peoples of the Americas were disrupted. Many Native Americans lost their lands and their lives, but some tribes became prominent regional power brokers who made the Europeans sit up and take notice.
The European colonial powers and Native American tribes fought a number of wars in America during the course of the 1600s and 1700s. Often the Europeans fought the Indians, or Native American tribes fought each other. At times the Indian tribes fought as allies of the rival European powers.
One of the main causes of these wars, which affected wide areas of North America – even the Illinois Country – was the desire to control the lucrative fur trade. Early in the French colonization of Canada, France allied itself with the Huron and Algonquin in Quebec and Ontario. These tribes were involved in ongoing feuds and wars with the League of the Iroquois, a confederation of five tribes or nations in New York, the Mohawk, the Oneida, the Onondaga, the Cayuga, and the Seneca.
France offered their native allies military assistance against the Iroquois because their allies supplied them with fur – especially beaver pelts – for sale in European markets. As early as 1603, French explorer Samuel de Champlain and his companions joined with France’s native allies in a raid on the Iroquois, which quickly led to an escalation of the conflicts in that part of America. This sparked a series of wars starting in 1628 between the Iroquois and the Huron and neighboring tribes in a struggle to dominate the fur trade.
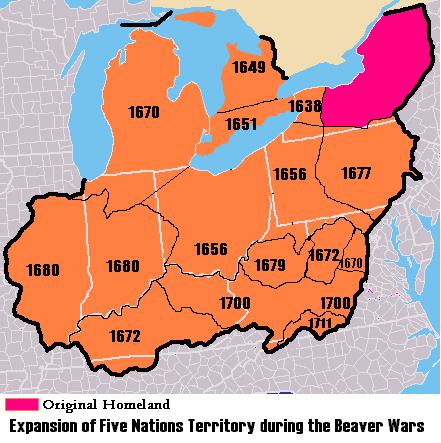
These wars are known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars, but they are also called the Beaver Wars. As the wars continued, the Iroquois League, supplied with European weapons by the Dutch and English, attacked both the neighboring tribes and French colonists. The Iroquois managed to subjugate or expel their neighbors, controlling their lands and hunting grounds, and expanding their power and influence as far west as the Illinois and Mississippi rivers. The high demand for beaver pelts severely depleted the beaver population in eastern North America, pushing Native Americans to seek further west and north to find beaver to hunt.

Inevitably, the westward expansion of the Iroquois League reached the Illinois Country, which they had seized by the mid-1600s. When Marquette and Jolliet first explored the Illinois Country in the 1670s, they found the Illiniwek tribes at war with the Iroquois. La Salle signed treaties with the Illini and Miami in 1681. In response to Iroquois expansion, the Miami in the Ohio Country and the Anishinaabe of southern Ontario formed confederacies and alliances with their neighbors. When the Iroquois destroyed a large Miami settlement and took large numbers of prisoners in 1689, the Miami sent to the Anishinaabe for help, and together they set an ambush for the Iroquois near modern South Bend, Ind., where the Iroquois suffered a decisive defeat. Unable to maintain their hold on the Illinois and Ohio regions, the Iroquois retreated and many of the local tribes were able to move back to their former homes.
By the end of the 1600s, the French adopted a new policy toward the Iroquois League, seeking to befriend them as a way to safeguard their control of the northern fur trade and to stop English colonial expansion. This new policy was cemented by the Great Peace of Montreal, signed in 1701 by the French and 39 Indian chiefs, thus bringing the Beaver Wars to an end. In the aftermath, the Ottawa and Pottawatomi tribes moved from Canada to Michigan, and the Illini were able to return to the Illinois Country.
In the late 1600s and the first half of the 1700s, the French in North America were involved in a series of wars with their rivals the British, and Native American allies also were caught up in the conflicts. However, these conflicts did not have much if any direct effect on the Illinois Country, which was never the scene of any military action during the wars. Prior to 1754 all of them – sometimes called the French and Indian Wars, or the Intercolonial Wars – started in Europe and then spilled over to North America.
However, in 1754, for the first time a war broke out in North America between the French and English colonies that then spilled over to Europe. In America, it is known as the French and Indian War since the Native American allies of France and England fought alongside the European colonists – but in Europe it is called the Seven Years War. Although the Illinois Country was again not a scene of battle, the outcome of the war was significant for the future of Illinois, because the French and Indian War resulted in the English conquest of half of France’s colonies on the mainland of North America, including the Illinois Country. (Spain acquired the other half, the vast province of Louisiana.) The French in Canada remember the French and Indian War as “the War of the Conquest.”
The French and Indian War ended with the signing of the Treaty of Paris on Feb. 10, 1763, when France gave up New France in Canada, New Orleans in Louisiana, and their forts, settlements, and fur trading outposts along the Illinois River Valley and elsewhere. Illinois then passed to British control – but French colonists and their families would maintain a presence in Illinois for some time to come.